[ps2id id=’background’ target=”/]
BACKGROUND
A thiazine-eosine buffered solution, Giemsa stain is designed to deliver coloration for type of cells. Giemsa’s solution is a mixture of methylene blue, eosin, and Azure B and available in a powder form. It can be used separately or in combination with a May-Grünwald Stain.
Aim: The aim of the experiment is to stain live and dead cells with Giemsa staining method.
[ps2id id=’requirements’ target=”/]
REQUIREMENTS
Cells: Cell suspension in an Eppendorf tube
Instrument: Light Microscope
Apparatus: Slides
Coverslip
Staining dishes
Chemicals: 1X PBS
Giemsa stain
May-Grünwald Stain (supplied as ready to use)
[ps2id id=’procedure’ target=”/]
PROCEDURE
Before starting the experiment, dilute Giemsa Stain 1:20 with deionized water. Place slides in May-Grünwald Stain for 5 minutes further, transfer slides in phosphate buffered saline for less than 2 minutes and keep slides in dilute Giemsa solution for 15-20 minutes. Rinse slides briefly in deionized water then Air dry and finally evaluate. After staining, observe the slides in light microscope.1
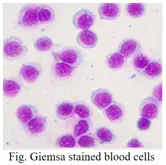
Observation
Figure 1 is the demonstration about the Giemsa stained blood cells.2 Live cells are in blue color and no dead cells were observed in the cell suspension.
[ps2id id=’conclusion’ target=”/]
CONCLUSION
Here, we performed Giemsa staining to investigate the differentiated live cells from dead cells.
[ps2id id=’references’ target=”/][ps2id id=’1′ target=”/]
REFERENCES
-
Giemsa stain, procedure no. GS-10. Available at sigmaaldrich.com.
-
AB Kadir R, Ariffin SHZ, Wahab RMA, Senafi S. Molecular characterisation of human peripheral blood stem cells. S Afr J Sci. 2012;108(5/6), Art. #939, 7 pages. http:// dx.doi.org/10.4102/sajs. v108i5/6.939.



